How To Install Gnu C++ Compiler
Several modernistic C++ features are currently missing from Visual Studio Express, and from the system GCC compiler provided with many of today's Linux distributions. Generic lambdas – besides known as polymorphic lambdas – are one such feature. This feature is, nonetheless, available in the latest versions of GCC and Clang.
The post-obit guide will aid you install the latest GCC on Windows, so you can experiment with generic lambdas and other cutting-edge C++ features. You'll need to compile GCC from sources, just that'due south not a trouble. Depending on the speed of your machine, yous can have the latest GCC up and running in as petty as 15 minutes.
The steps are:
- Install Cygwin, which gives us a Unix-like environment running on Windows.
- Install a set of Cygwin packages required for edifice GCC.
- From within Cygwin, download the GCC source lawmaking, build and install information technology.
- Test the new GCC compiler in C++xiv style using the
-std=c++xivselection.
[Update: Equally a commenter points out, you can also install native GCC compilers from the MinGW-w64 project without needing Cygwin.]
1. Install Cygwin
First, download and run either the 32- or 64-bit version of the Cygwin installer, depending on your version of Windows. Cygwin's setup magician volition walk y'all through a series of steps. If your car is located behind a proxy server, make certain to cheque "Use Internet Explorer Proxy Settings" when yous get to the "Select Your Net Connection" step.
When you reach the "Select Packages" step (shown below), don't bother selecting whatsoever packages however. Just go ahead and click Next. We'll add additional packages from the control line later.
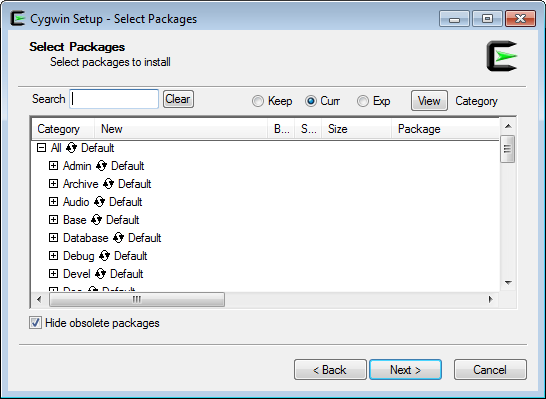
Afterwards the Cygwin installer completes, information technology's very important to keep the installer effectually. The installer is an executable named either setup-x86.exe or setup-x86_64.exe, and y'all'll need it to add or remove Cygwin packages in the hereafter. I propose moving the installer to the aforementioned folder where yous installed Cygwin itself; typically C:\cygwin or C:\cygwin64.
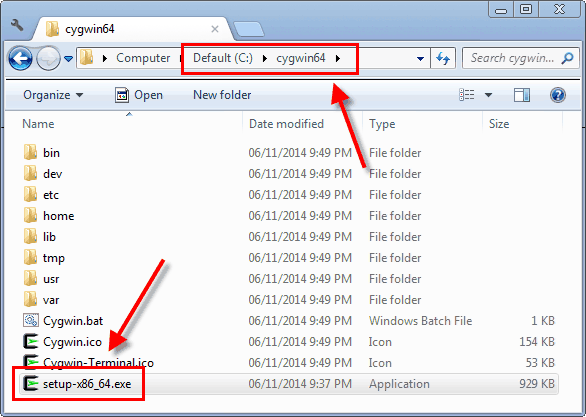
If you already have Cygwin installed, it'due south a good thought to re-run the installer to make certain it has the latest available packages. Alternatively, you can install a new example of Cygwin in a different folder.
ii. Install Required Cygwin Packages
Next, you'll need to add together several packages to Cygwin. Y'all can add them all in one fell swoop. Simply open a Command Prompt (in Windows), navigate to the folder where the Cygwin installer is located, and run the following command:
C:\cygwin64>setup-x86_64.exe -q -P wget -P gcc-g++ -P make -P diffutils -P libmpfr-devel -P libgmp-devel -P libmpc-devel 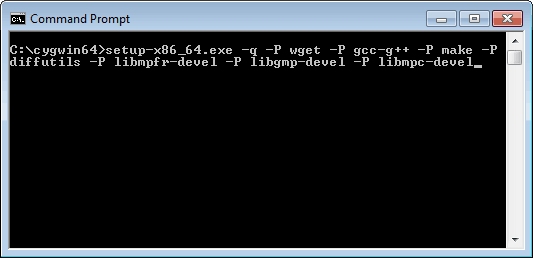
A window will popular up and download all the required packages along with their dependencies.
At this point, you now have a working GCC compiler on your arrangement. Information technology's not the latest version of GCC; it's any version the Cygwin maintainers chose as their system compiler. At the time of writing, that's GCC four.viii.3. To become a more than contempo version of GCC, you'll accept to compile it yourself, using the GCC compiler you already take.
3. Download, Build and Install the Latest GCC
Open a Cygwin terminal, either from the Start menu or by running Cygwin.bat from the Cygwin installation folder.
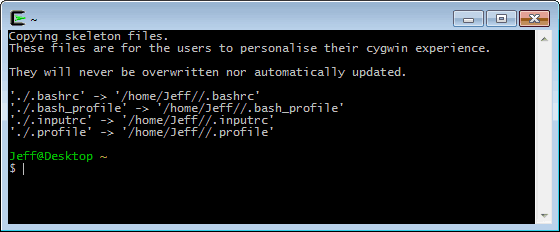
If your machine is located behind a proxy server, you must run the following command from the Cygwin terminal earlier proceeding – otherwise, wget won't work. This pace is not needed if your machine is directly connected to the Cyberspace.
$ export http_proxy=$HTTP_PROXY https_proxy=$HTTP_PROXY ftp_proxy=$HTTP_PROXY To download and extract the latest GCC source code, enter the following commands in the Cygwin terminal. If you're post-obit this guide at a later appointment, there will surely exist a more recent version of GCC available. I used 4.nine.2, but yous can employ any version you similar. Keep in mind, though, that information technology's always best to have the latest Cygwin packages installed when edifice the latest GCC. Be patient with the tar control; it takes several minutes.
$ wget http://ftpmirror.gnu.org/gcc/gcc-iv.9.2/gcc-4.ix.two.tar.gz $ tar xf gcc-4.ix.two.tar.gz That will create a subdirectory named gcc-4.9.2. Next, we'll configure our GCC build. As the GCC documentation recommends, information technology'southward best to configure and build GCC in another directory outside gcc-four.9.2, so that's what we'll practise.
$ mkdir build-gcc $ cd build-gcc $ ../gcc-4.9.2/configure --program-suffix=-4.9.ii --enable-languages=c,c++ --disable-bootstrap --disable-shared Here'southward a description of the control-line options passed to configure:
-
The
--plan-suffix=-iv.nine.2option means that one time our new GCC is installed, nosotros'll run it asg++-4.9.2. This will make it easier for the new GCC compiler to coexist alongside the system GCC compiler provided past Cygwin. -
The
--enable-languages=c,c++option means that merely the C and C++ compilers will be built. Compilers for other languages, such as Fortran, Coffee and Go, will exist excluded. This volition save compile time. -
The
--disable-bootstrapoption means that we only want to build the new compiler one time. If we don't specify--disable-bootstrap, the new compiler will exist built 3 times, for testing and functioning reasons. However, the arrangement GCC compiler (iv.8.iii) provided by Cygwin is pretty recent, so--disable-bootstrapis expert enough for our purposes. This volition save a significant amount of compile fourth dimension. -
The
--disable-sharedoption means that nosotros don't desire to build the new standard C++ runtime library as a DLL that's shared with other C++ applications on the system. It'southward totally possible to make C++ executables work with such DLLs, simply information technology takes care not to introduce conflicts with C++ executables created past older or newer versions of GCC. That's something distribution maintainers need to worry about; not u.s.a.. Let's just avoid the additional headache. -
By default, the new version of GCC will be installed to
/usr/localin Cygwin'south virtual filesystem. This volition make it easier to launch the new GCC, since/usr/local/binis already listed in Cygwin'due southPATHenvironment variable. However, if you're using an existing Cygwin installation, it might show difficult to uninstall GCC from/usr/locallater on (if y'all then choose), since that directory tends to contain files from several different packages. If you prefer to install the new GCC to a different directory, add the choice--prefix=/path/to/directoryto the aboveconfigurecommand.
We're not going to build a new Binutils, which GCC relies on, because the existing Binutils provided by Cygwin is already quite contempo. We're also skipping a couple of packages, namely ISL and CLooG, which means that the new compiler won't be able to use whatever of the Graphite loop optimizations.
Next, we'll actually build the new GCC compiler suite, including C, C++ and the standard C++ library. This is the longest step.
$ make -j4 The -j4 option lets the build procedure spawn up to 4 child processes in parallel. If your machine's CPU has at to the lowest degree four hardware threads, this pick makes the build process run significantly faster. The main downside is that it jumbles the output messages generated during the build procedure. If your CPU has even more hardware threads, you tin specify a higher number with -j. For comparison, I tried various numbers on a Xeon-based auto having 12 hardware threads, and got the following build times:
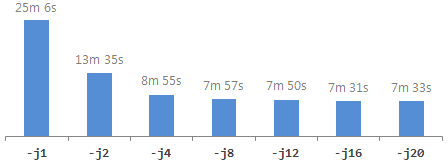
Be warned: I encountered a segmentation fault the first time I ran with -j4. Bad luck on my part. If that happens to you, running the same control a second time should allow the build procedure to end successfully. Also, when specifying higher numbers with -j, there are often strange fault messages at the end of the build procedure involving "jobserver tokens", but they're harmless.
One time that's finished, install the new compiler:
$ make install $ cd .. This installs several executables to /usr/local/bin; it installs the standard C++ library's include files to /usr/local/include/c++/4.9.2; and it installs the static standard C++ library to /usr/local/lib, among other things. Interestingly, information technology does not install a new standard C library! The new compiler will continue to apply the existing system C library that came with Cygwin.
If, subsequently, you decide to uninstall the new GCC compiler, you lot have several options:
- If you lot installed GCC to a directory other than
/usr/local, and that directory contains no other files, you tin simply delete that directory. - If you installed GCC to
/usr/local, and in that location are files from other packages mixed into the aforementioned directory tree, you lot can run thelist_modifications.pyscript from this post to decide which files are safe to delete from/usr/local. - You can simply uninstall Cygwin itself, past deleting the
C:\cygwin64folder in Windows, along with its associated Start carte entry.
four. Test the New Compiler
All right, let's compile some code that uses generic lambdas! Generic lambdas are part of the C++xiv standard. They let y'all pass arguments to lambda functions as auto (or whatsoever templated type), like the i highlighted below. Create a file named test.cpp with the following contents:
#include <iostream> int main() { auto lambda = [](auto x){ return x; }; std::cout << lambda("Howdy generic lambda!\due north"); return 0; } Yous can add files to your home directory in Cygwin using any Windows-based text editor; just salvage them to the folder C:\cygwin64\home\Jeff (or similar) in Windows.
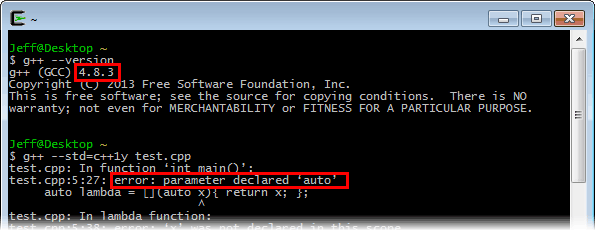
Outset, let'south see what happens when we try to compile information technology using the system GCC compiler provided by Cygwin:
$ g++ --version $ g++ -std=c++1y test.cpp If the organisation compiler version is less than 4.ix, compilation will fail:
Now, let's attempt it once more using our freshly built GCC compiler. The new compiler is already configured to locate its include files in /usr/local/include/c++/4.ix.ii and its static libraries in /usr/local/lib. All we need to do is run it:
$ g++-iv.9.two -std=c++14 exam.cpp $ ./a.exe 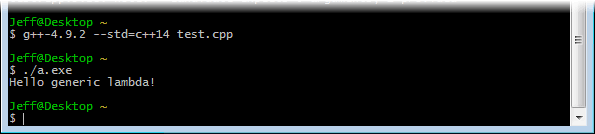
Information technology works!
Source: https://preshing.com/20141108/how-to-install-the-latest-gcc-on-windows
Posted by: stinsoncappor.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Install Gnu C++ Compiler"
Post a Comment